Perfect vision is achieved after light rays are refracted or bent by the cornea to be focused onto the retina. The retina’s work is to convert rays of light into impulses which are inturn sent to the brain. The brain then recognizes these as images.
If these rays of light will not focus well on the retina, a blurry image will be created (refractive error). These refractive errors might be caused by an imperfect cornea or eyeball.
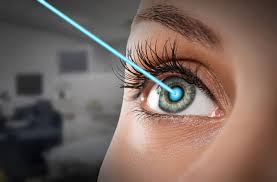
These errors are corrected by contact lenses, glasses or refractive surgeries. These focuses light onto the retina and tries to correct the errors.
LASIK surgery can be used to correct;
Myopia (near sightedness) – this is when only close object appear distinct and clear but far object appear blurred
Hyperopia (far sightedness) – a condition whereby only objects that are far are distinct but closer objects appear blurred.
Astigmatism – A condition where images viewed aren’t clear (blurred) whether they are near or far.
Presbyopia – At the ages of 40 to 50, visions might become more difficult and this condition is known as the aging eye. This condition can be corrected through LASIK surgery other refractive surgery. Reading glasses or bifocals can also be used.
LASIK is just one of the different surgical techniques used to reshape the cornea so as the light passing through it is focused onto the retina and is a complex irreversible process.
A person who deals with surgical eye treatment is known as an ophthalmologists and these medical doctors are the ones that perform LASIK procedures.
A refractive eye surgeon first performs an examination of the eye and your eye prescription history is checked. Contact glasses should not be worn two weeks prior to the evaluation; Rigid gas permeable lenses three weeks and hard lenses four weeks because these might alter measurements in the examination.

This surgery is painless due to anesthetic eye drops that the surgeon applies to the eye at the beginning of the operation.
A protective flap is created after the anesthesis to access the tissues deeper in the cornea by an instrument called a microkeratome or femtosecond laser. Invisible laser light, which is controlled by a computer, reshapes the inner layer of the cornea while an eye-tracking device tracks eye movements to make sure that perfect correction is achieved.
The flap is then aligned to its initial position followed by protective shields. These prevents the patient from rubbing and disturbing the natural healing of the flap. It takes hours for the flap to heal securely but the operation will take about 10 minutes to complete.
A patient may experience mild burning after the surgery. Blurred vision will be experienced afterwards but vision improves considerably the next day.
Complications, though minimal, can be experienced. They may include; incomplete or irregular flaps, in growth of cells under flap and irregular healing results. These can be corrected by surgical removal and corneal transplant respectively. Eye infections or chronic dry eyes might also be experienced.
Safety measures like; avoiding hot tubs, swimming, whirlpools and swimming should be avoided for at least two weeks after the surgery.
Driving should be avoided until vision has improved and any unusual side effects should be immediately reported to the doctor.